What Is Net Metering and How Does It Work?
- Home Page
- Energy 101: Resources to Help Understand Energy
- Energy Innovation
- What Is Net Metering and How Does It Work?
Net metering is a billing system that tracks the difference between the energy your solar panels produce and the energy you consume, crediting you for excess production or billing you for additional usage.
Table of contents:
- How Does Net Metering Work?
- What Are the Benefits of Net Metering?
- What Are the Drawbacks of Net Metering?
- What Are Alternatives to Net Metering?
How Does Net Metering Work?
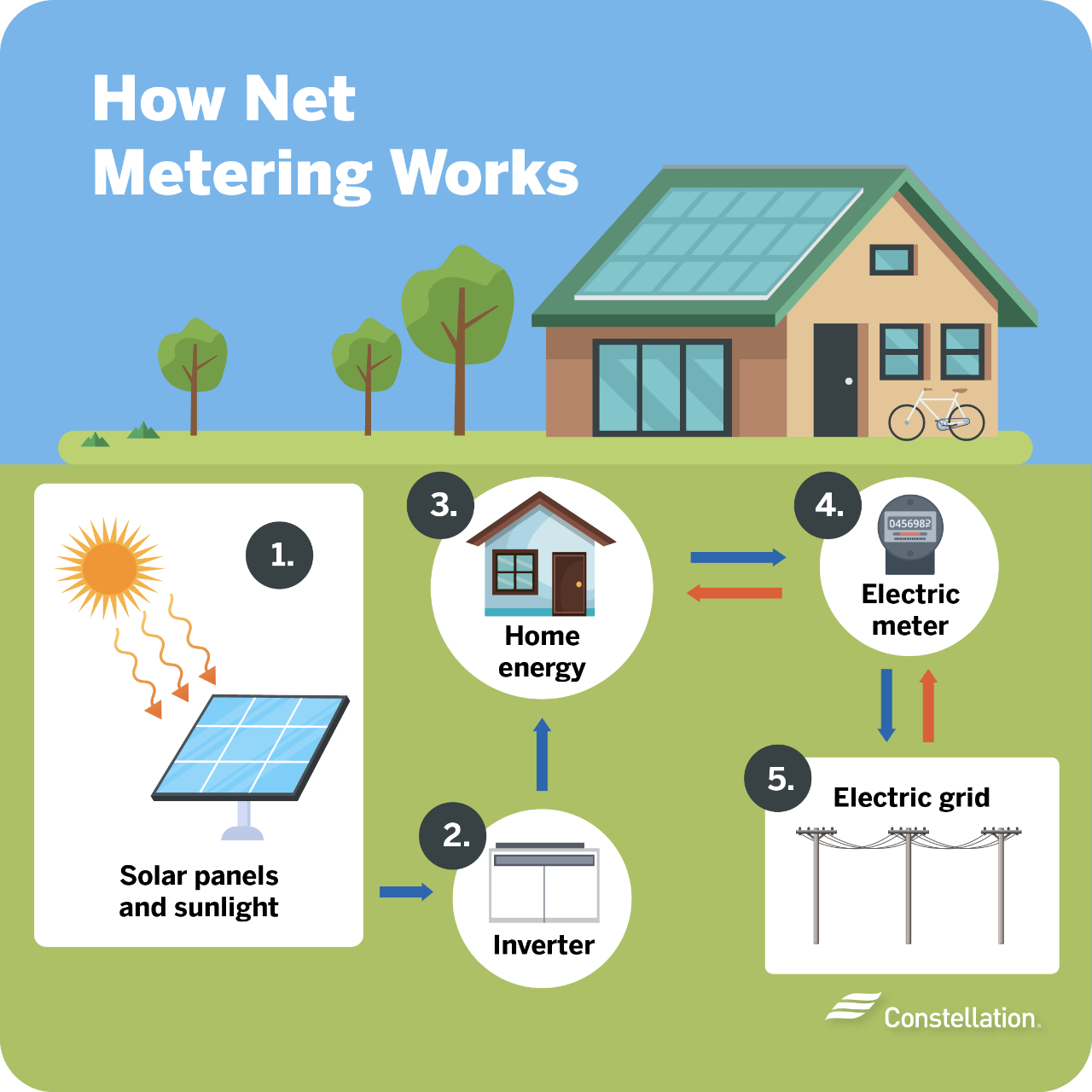
Solar net metering measures your power consumption against the power your solar panels produce. When you produce more solar energy than you use, the difference is credited back to you. On days when you are using more energy than your solar panels are producing, you draw against those credits. At the end of the billing cycle, you may have a net credit on your bill, or you may have a balance to pay.
What are the Benefits of Net Metering?
Net metering provides several key benefits for homeowners using solar energy:
- Cost Savings: You only pay for the electricity used beyond what your solar panels produce, potentially significantly reducing your electricity bills.
- Financial Viability: Net metering makes investing in solar power financially attractive by maximizing your return on investment.
- Earning Potential: You can receive credits for excess energy your solar panels generate, effectively earning you savings or even money back on your energy bill.
- Encourages Solar Adoption: Net metering incentives motivate more homeowners to install solar panels, supporting wider renewable energy adoption and reducing dependence on traditional energy sources.
By offsetting your energy costs and potentially providing financial returns, net metering enhances the practicality and appeal of solar energy systems for homeowners.
What are the Drawbacks of Net Metering?
The drawbacks of net metering include:
- Solar net metering is not available in all locations or from all electricity providers
- You need to connect your solar panel system to the grid
- You don’t get paid and don’t earn money from the power you produce
- Without time-of-use billing, your net metering credits are not adjusted according to when you produce power
What are Alternatives to Net Metering?
The three alternative approaches to net metering include buy all/sell all, net billing, and solar self consumption. Let’s explore each option in detail:
Buy all/sell all
In this scenario, you continue to buy all the power you use from your utility company or electricity provider. What is different is that a second meter is installed to track your power generation, and all the excess power you produce is sold back to the utility or provider. The drawback here is that you buy power at the retail rate, but sell it at wholesale.
Net billing
With these kinds of programs, you sell any solar energy you don’t use back to your utility company or electricity provider. Instead of being paid directly, the value of the power you sell is credited on your utility or electricity bill. You will, of course, pay for all the power you buy off the grid.
Solar self-consumption
You always have the option of being both the producer and the consumer of the power you generate from your solar panel system. You can choose to be completely independent from the grid, using only the power you generate, or you can have parallel systems and only use the grid when you need it.
Net Metering FAQs
Can you get paid from net metering?
You don’t get cash in hand with solar net metering. You do get a credit for the energy you produce in excess of what you use.
Which states have net metering?
Most states have net metering policies in place. The exceptions are South Dakota, Tennessee, and Alabama. Texas and Idaho don’t have state-wide policies. Utah and Arizona don’t have net metering but do offer alternatives. The space is changing fast, so check with your electricity provider for the most up-to-date information.
Do net metering credits expire?
You will need to check the policies of your specific electricity provider. In most cases, credits expire annually or according to a specific date in your agreement. In a few states and localities, credits may expire every month.
What is virtual net metering?
You don’t need to buy, install and maintain a solar panel system to get the benefits of solar net metering. Shared solar, wherein several households or investors pool their resources to put in the system, can benefit from virtual net metering. You get a bill credit for your share of the total energy fed back into the grid that reflects your ownership percentage of that shared system.
Does net metering only apply to solar?
While net metering is associated with solar power, it isn’t limited to that energy source. Any power you generate, which could be by wind, hydro, or animal waste from biogas, to name a few, is eligible for net metering if you can effectively connect your power generation to the grid.
Don’t Have Solar but Want to Lower Your Energy Bills?
Installing solar panel systems for net metering is not practical for everyone. That doesn’t mean you can’t use renewable energy. In many states, you have a choice of retail electricity providers, so you may be able to trim your energy costs by selecting the right company. Constellation has a variety of home energy options that give you a choice of energy plans, including fixed-rate plans.