These basic chargers plug into a regular 120-volt household outlet. Many EV manufacturers provide a level 1 charger and cable that connects your EV directly to your house power as standard equipment. They are an inexpensive option if you don’t drive far and can charge the vehicle for an extended period, such as overnight.
Charging your EV this way is very slow—you recover about 3 to 5 miles of range for every hour of charging. The cost to charge your EV with a level 1 charger depends on the rate you pay for electricity and the capacity of your car’s battery. To make the math simple, if you pay $0.10 per kWh and your EV battery capacity is 100 kWh, the cost of the energy to charge will be $10.
Level 2 chargers
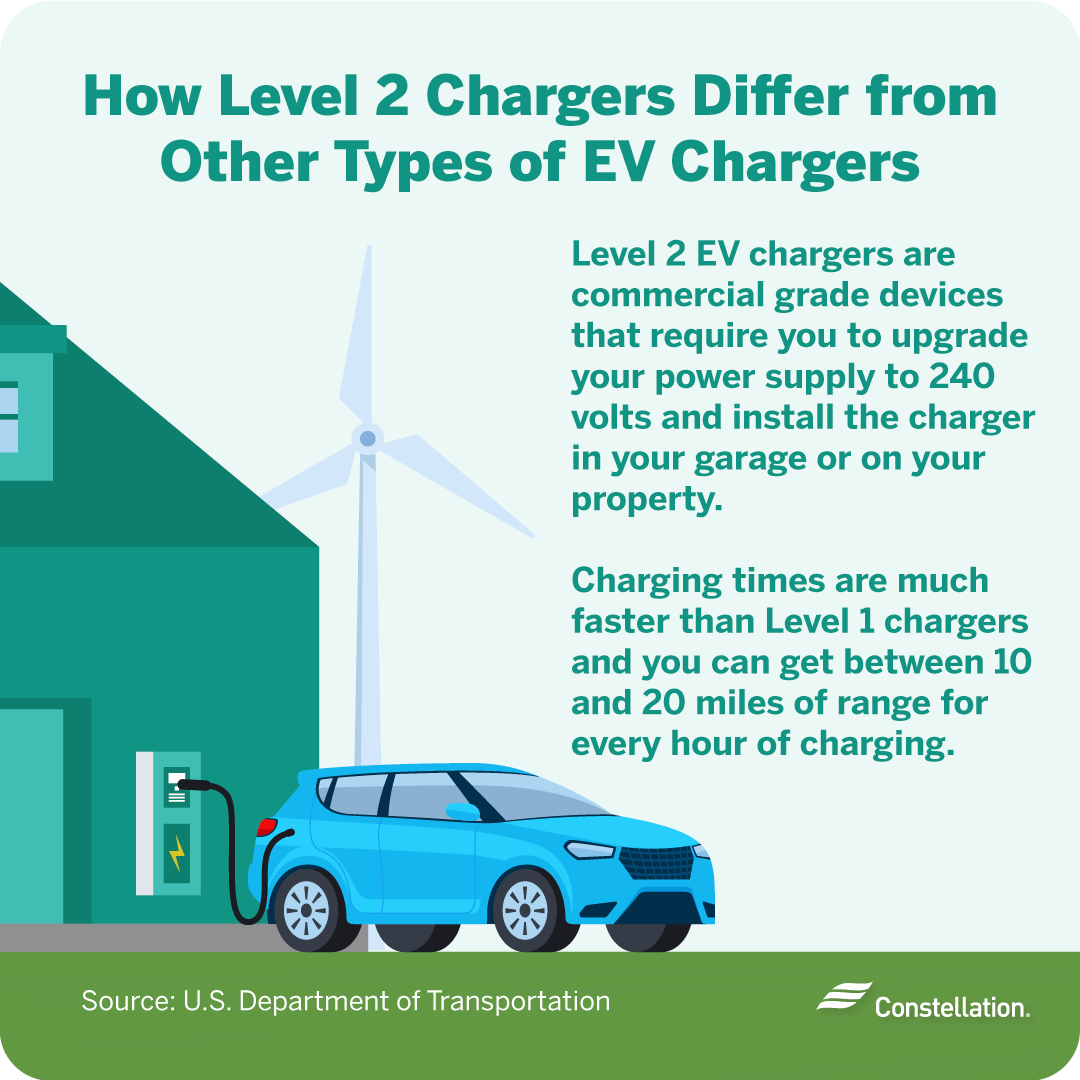
If you need a faster way to charge, consider a level 2 charger. If you commute a longer distance every day, slower overnight charging from a level 1 charger might not give you the range you need. These commercial grade devices require that you upgrade your power supply to 240 volts and install the charger at your property. You may find the convenience to be well worth it.
Charging times are much faster. You can get between 10 and 20 miles of range for every hour of charging. After you have paid for installation, you will likely see your electricity bill increase due to higher usage from charging at home. Specialized rate plans for EV owners are available in select markets.
DC fast chargers (level 3)

Level 3 chargers are the fastest option, but they are generally impractical for homeowners. Few residential neighborhoods supply the 400v power these devices require. The cost and complexity of installation, along with local laws that may prohibit them, are an additional hurdle. You may find the cost of a level 3 charger to be higher than the cost of your EV.
You are most likely to encounter level 3 chargers in public charging stations. They require high voltage DC service, between 400 and 1000 volts. Instead of relying on your car to convert AC power to DC, they pump DC power directly into your battery. They can fully charge your EV in 20 minutes to an hour.
You can expect to pay more for the convenience of a faster charge. The charges vary by network, location and time of day. A Kelly Blue Book article from July 2024 quotes a price of $0.49 per kWh off peak and $.056 per kWh during high demand times.
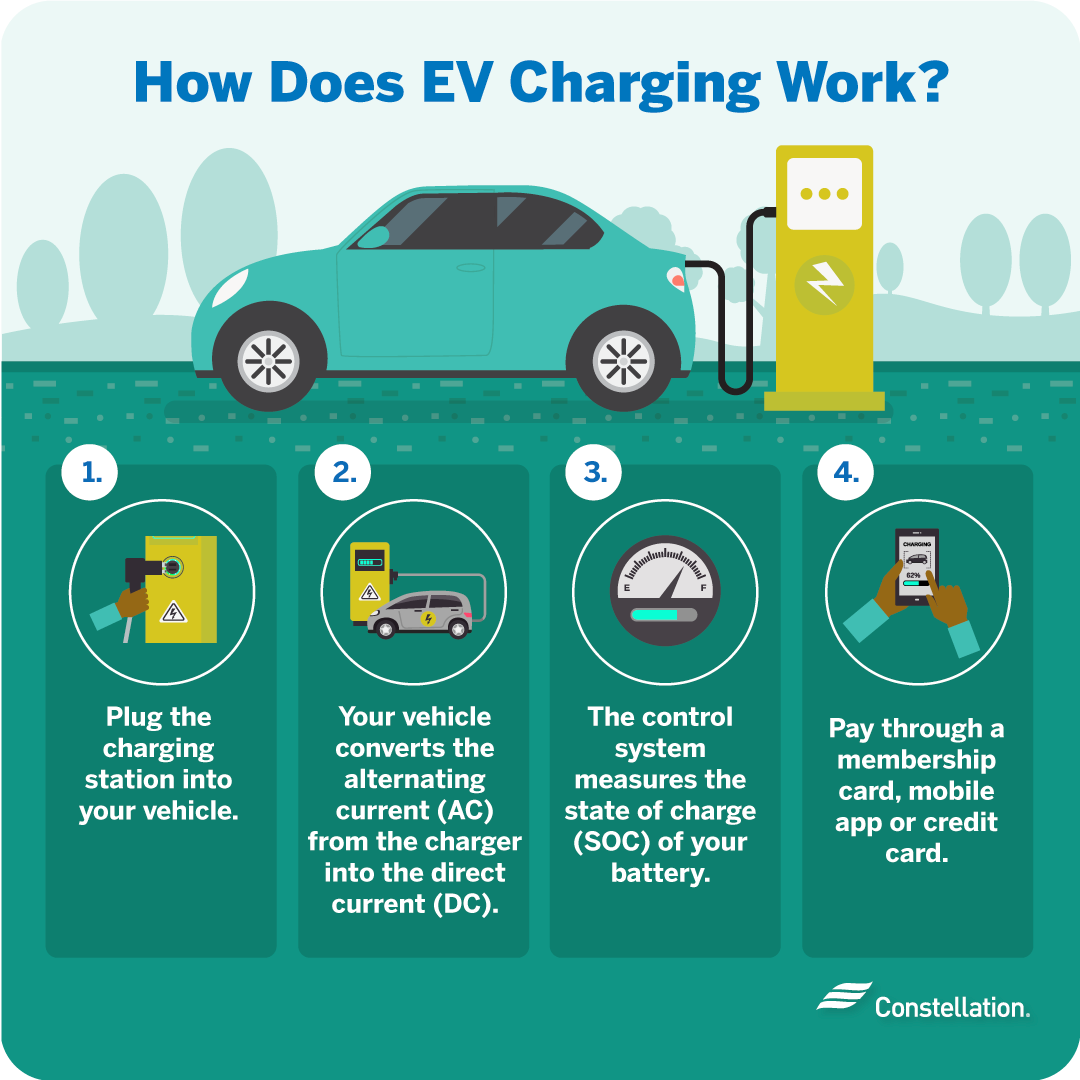
Basic components of EV chargers
In understanding how EV charging stations work, start with understanding the components:
- Power supply: Connects to the grid, or potentially a renewable energy source.
- Charging cable: Brings power from the supply to your vehicle.
- Plug or Connector: Plugs into your vehicle’s charging port.
- Control system: Regulates the safe and efficient flow of electricity into your vehicle.
- Communication system: Connects the computer in the charging station with the computer in your vehicle to manage charging speeds and levels.
If you decide to install a level 2 EV charger in your home, you will want to understand how these components work together to ensure a safe and controlled flow of electricity that protects your battery from damage. If you are charging your car at home, you want an easy-to-use EV charger that keeps you informed about the charging status of your EV.
How do public EV charging stations work?
How do EV charging stations work? Typically, you have to pay to use a public EV station. Membership networks charge a monthly fee, but most are pay-as-you go.
You should charge only up to 80% of your battery capacity. Charging is much slower over the last 20%. And be sure to check the price before you plug in.
Are EV charging stations free?
Yes, you can find free EV charging stations but they are becoming rare. More states started to impose taxes or flat fees for public EV charger use. You can expect to pay by the minute, by the kWh or a blend of both. Some networks charge you a membership fee. Some add a charging session fee and a “dwell time” fee for the time you remain parked at the charger after charging ends.
Next steps in your EV charging journey: set up your home charging solution
While it is vital to understand your EV charging options and how they work, you will likely settle into a routine and methods that are right for you.
For most people, charging at home and using home charger installation services like the one provided by Constellation can be a cost effective and the most convenient way to keep your EV battery topped up.